
Ī PubMed literature review was conducted to include articles published up to February 2016. More recently, however, two prospective, controlled therapeutic trials were unable to confirm the previous findings and demonstrated that lower intensity anticoagulation (INR: 2.0-3.0) sufficed in preventing recurrent thromboembolic events. Previously, older retrospective studies suggested high-intensity anticoagulation to an INR > 3 in order to prevent recurrent thromboembolic events. Various studies have shown patients with APS require long-term anticoagulation with warfarin to reduce recurrent thromboses, morbidity, and mortality. It has been suggested the qualities of these studies are poor due to low adherence to classification criteria and standardization of laboratory tests. The thrombotic recurrence rates in APS patients have been suggested to range between one and 16/100 patients/year in various studies applying different classification criteria and therapeutic ranges. Literature has supported positive aPL may correlate with thrombotic risk. Studies have shown APS patients have more frequent thrombotic recurrences than non-APS patients. Diagnosis of aPL syndrome is based on the Sydney criteria, which is defined as either proven vascular thrombosis (venous, arterial, or small vessel) or pregnancy morbidity and the presence of aPL antibodies (anticardiolipin antibodies, beta2-glycoprotein antibodies, or lupus anticoagulant) on two or more occasions. A longer-than-normal PT can be caused by treatment with blood-thinning medicines, such as warfarin or, in rare cases, heparin.Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an acquired systemic autoimmune disease characterized by thrombotic events, pregnancy complications, and the presence of antiphospholipid (aPL) antibodies.This is a life-threatening condition in which your body uses up its clotting factors so quickly that the blood cannot clot and bleeding does not stop. A longer-than-normal PT can also mean that you have disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC). It can also mean a lack of vitamin K liver disease, such as cirrhosis or that a liver injury has occurred. A longer-than-normal PT can mean a lack of or low level of one or more blood clotting factors (factors I, II, V, VII, or X).Prothrombin times are also kept at longer times for people with artificial heart valves, because these valves have a high chance of causing clots to form. The warfarin dose is changed so that the prothrombin time is longer than normal (by about 1.5 to 2.5 times the normal value or INR values 2 to 3). In some labs, only the INR is reported and the PT is not reported. Using the INR system, treatment with warfarin (Coumadin) will be the same. A value that isn't in the normal range may still be normal for you.Ī method of standardizing prothrombin time results, called the international normalized ratio (INR) system, has been developed so the results among labs using different test methods can be understood in the same way. Your doctor will also look at your results based on your age, health, and other factors. Your lab report should show the range that your lab uses for each test. An increase in the use of the clotting factors.Īn abnormal prothrombin time is often caused by liver disease or injury or by treatment with blood thinners.Įach lab has a different range for what's normal.Other substances, called inhibitors, that affect the clotting factors.The absence of any of the clotting factors.
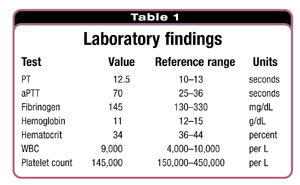


It lets your doctor understand results in the same way even when they come from different labs and different test methods. INR (international normalized ratio) stands for a way of standardizing the results of prothrombin time tests, no matter the testing method. PT is also used to check whether medicine to prevent blood clots is working.Ī PT test may also be called an INR test. A prothrombin time test can be used to check for bleeding problems. Prothrombin time (PT) is a blood test that measures how long it takes blood to clot.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
